Linux basics commands
Being a programmer or a simple user on Linux, it’s good to know the basic commands on Linux. Maybe you think ok I can handle this using my Linux GUI, but not.
On this section we will see the commands that you need to know as a newbie on Linux.
Content:
- Introduction
- Super user mode(sudo)
- What is APT, using apt-get
- What’s inside a folder
- Navigate throw directories with cd
- Create alias in .bashrc file
- how to move a file or directory ? (mv)
- create a directory (mkdir)
- how to copy a file or directory ?(cp)
- Linux permissons and ownership
- where is installed? (which)
- how to find a file or folder?
Introduction
https://blastcoding.com/en/linux-basic-commands/#introductionParticularly I use Linux-mint on my machine, so all commands you are going to see here, works on Ubuntu distributions and others that derives from Debian.
All commands were tested on my machine first, so if you found something wrong you can communicate with me via Twitter or Facebook page, links at footer page.
It’s probably that quantity of command in this page rise, as soon I use new commands and been considered necessary for Linux users.
Super User Mode (Sudo)
https://blastcoding.com/en/linux-basic-commands/#super_user_sudoLinux come with a specific command to run a process as super user, this command is sudo, at least on Debian distributions, and derives.
You can use sudo at the beginning of any command to run this one as super user. Syntax:
sudo [command] [command option]
May run sudo all time without using, sudo every time you want to run ca comand with sudo -i command.
sudo -i
What is APT? Using apt-get
https://blastcoding.com/en/linux-basic-commands/#apt-getAPT (Advance packaging tool) is the way we can interact with the package system of Debian, we can install, uninstall, inclusive upgrade our Linux version.
You can install a program with the following syntax:
sudo apt-get install program_name
If you want to uninstall a program:
sudo apt-get remove program_name
Generally you can search on internet and install a program downloading a .deb file and clicking on it. Sometimes we need to search for a program on the package manager. We could do that with the following line:
sudo apt-get search program_name
Linux allow us to update the list on the package manager, running this command we make sure that we are installing the last version compatible with our Linux version.
sudo apt-get update
What’s inside a folder
https://blastcoding.com/en/linux-basic-commands/#directory_contentIn Case we need known the content inside a folder, we could use 2 commands.
dir
https://blastcoding.com/en/linux-basic-commands/#dirThe easiest way to get the content inside a directory is using dir.
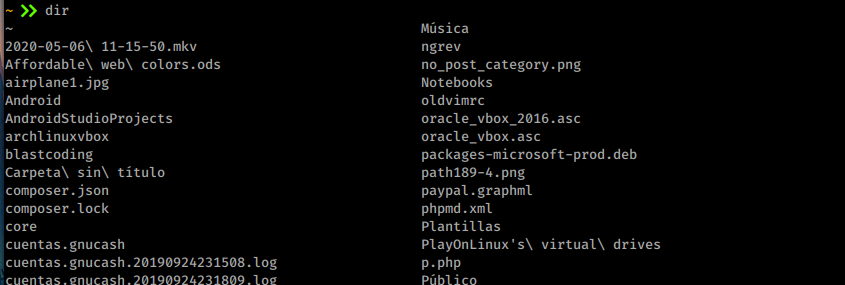
You may add different parameters to dir, like dir -S, dir -A, dir -F.
Lets take a deep look to these opotional commands:
Command dir -A allow us to see hidden files:
dir -A
¿ What another optional commands we have with dir?
- -F: adding -F after dir makes a distinction with folders adding a slash (/) at end.
- -S order per size files and directories.
- -l show us detailed information of files and folder, permissions and what user is owner.
Dir has more options, but these are the most useful.
Also, this options can be combined:
dir -l -S
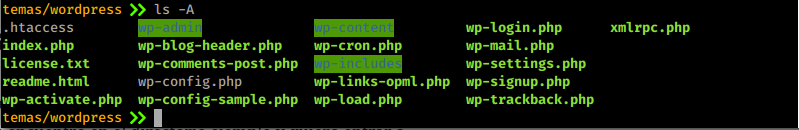
ls
https://blastcoding.com/en/linux-basic-commands/#lsList the content inside a directory, this command do the same thing that does dir and has the same options.
Navigate throw directories with cd
https://blastcoding.com/en/linux-basic-commands/#cd_commandLike title side we can navigate through directories with cd, example if I’m inside a folder like (mydir) and want to enter inside a folder that is inside called lemon(mydir/lemon/) I only need to run this command:
cd lemon
You can use full path too, like cd /var/www/html, ¿how cd knows that you are using a full path? That depends on if you are using ( / ) or not, if you use slash at the beginning you are using a fullpath if not you are using a localpath.
If im in mydir/lemon/ ¿how can I return to mydir folder? You can use cd ..
cd ..
We can go directly to our user folder with :
cd --
Its not practical remember all time a complete route to a folder, we will resolve that with Aliases.
Creating an alias in .bashrc file
https://blastcoding.com/en/linux-basic-commands/#creating_aliases_in_bashFirst we have to open the .bashrc file that is in user directory
cd --
To open .bashrc file we can use nano cause come with Linux, or we can open it with vim that is a lightweight editor.
sudo nano .bashrc
Lets add our alias at the end of .bashrc file:
.bashrc filealias sites="cd /var/www/html"
As you can see now sites will open /var/www/html folder
You can save your file with ctrl + o and ctrl + x to leave.
¿How to move a file or directory? (mv)
https://blastcoding.com/en/linux-basic-commands/#move_files_with_mvYou can move a file or directory with mv, also mv permit us to change de file or directory name.
Sintaxis / Sintaxmv [archive_path] [desteny_path]
¿How to create a directory? (mkdir)
https://blastcoding.com/en/linux-basic-commands/#mkdirCommand mkdir permit us create a directory depending on path directory.
Example:
mkdir dis
Its make a folder where we are located, otherwise if I specified a full path it creates there.
mkdir /var/www/html/proyectonuevo
¿How to copy files and folders? (cp)
https://blastcoding.com/en/linux-basic-commands/#cpSometimes we need to copy a file or folder, we cold do this with cp command:
Sintaxis / Sintaxcp [file_path] [destination_path]
example:
~: cp proyectos/carpetavieja proyectos/carpeta nueva
Permissons on Linux
https://blastcoding.com/en/linux-basic-commands/#permissonsGive permissons to a propietary or a group is a common practice on Linux, so its good to know the basics, chown and chmod.
¿Who owns what? Chown
https://blastcoding.com/en/linux-basic-commands/#chownDefine who is the owner or proprietary of a file or folder is something that you may do not needed, if you are not a programmer you may skip permissions part, chown and chmod.
Coming Back to this sometime we need to change the owner, who can create, modify, delete this.
An example of this is the super user if you use again ls -l you can see the owner. If we go to root and run ls -l you can see that all folders have one owner(root, the super user).
This also define access of programs like Apache server to a folder or file, in the following example Apache can make changes on all inside WordPress folder, this is recommended in a WordPress site, so you can update plugins, and add new themes.
chown www-data:www-data /var/www/html/micarpeta
I’m giving permissions to www-data group and www-data as the owner.
Permissons chmod
https://blastcoding.com/en/linux-basic-commands/#chmodYou can change write,read, excecute permisons with chmod
Command chmod uses 3 digits to known, who have permissons to.
- Owner (propietary)
- Group (grupos of users that have permissons)
- World (everyone who have access)
example:
chmod 777 mydocs
Besides using numbers you can use letters here a table with both.
| # | Permission | rwx |
|---|---|---|
| 7 | read, write and execute | rwx |
| 6 | read and write | rw- |
| 5 | read and execute | r-x |
| 4 | read only | r– |
| 3 | write and execute | -wx |
| 2 | write only | -w- |
| 1 | execute only | –x |
| 0 | none | — |
We can set same permissions to all files and folder inside one folder with -R option. Where -R is recursively.
chmod 777 -R mydocs
There is a lot more about chmod but this is the basic.
¿Where is installed? (which)
https://blastcoding.com/en/linux-basic-commands/#whichWith which command we can know where is installed a program, these command is particularly useful if you don’t know where to search.
which firefox

As you can see running the command show us where Firefox is located.
¿How to find a file or directory?(find)
https://blastcoding.com/en/linux-basic-commands/#findYou may use command find to search for a file or directory, if you use it as in the syntax example you will search locally
find [file_name]
In order to search in machine you need to use / plus -name before the file_name or directory_name
find / -name [file_name]
We are using name to search by name and is an optional command that we can use with find.
Optional commands
| -type [*] | type para el tipo de archivo |
| -name | name para el nombre del archivo |
| -size | size para ver el tamaño del archivo |
| -empty | archivos vacios |
| -user | user para saberel dueño del archivo |
posible values of * in -type:
b – block (buffered) special
c – character (unbuffered) special
d – directory
p – named pipe (FIFO)
f – regular file
l – symbolic link
s – socket
D – door (Solaris)
We could use these command together
find -type f -name '*.pngWe



